Hair and scalp infections can cause a range of symptoms, from mild irritation to more severe inflammation and hair loss. These infections can be caused by various pathogens, including fungi, bacteria, and viruses. Understanding the common types of hair infections, their symptoms, treatment options, and prevention methods is crucial for maintaining scalp health and hair vitality. Here’s a comprehensive overview of hair infections:
Common Types of Hair Infections
- Tinea Capitis (Scalp Ringworm)
- Cause: A fungal infection caused by dermatophytes.
- Symptoms: Scalp ringworm presents as scaly, circular bald patches that may be itchy and inflamed. It can also lead to swollen lymph nodes and fever.
- Treatment: Oral antifungal medications are typically required, as topical treatments are usually not effective for scalp ringworm.
- Folliculitis
- Cause: Inflammation of hair follicles, usually caused by a bacterial infection (often Staphylococcus aureus).
- Symptoms: Red, swollen bumps around hair follicles that can be itchy or tender. Severe cases may lead to crusty sores and scarring.
- Treatment: Mild cases often resolve on their own, but more severe infections may require topical or oral antibiotics.
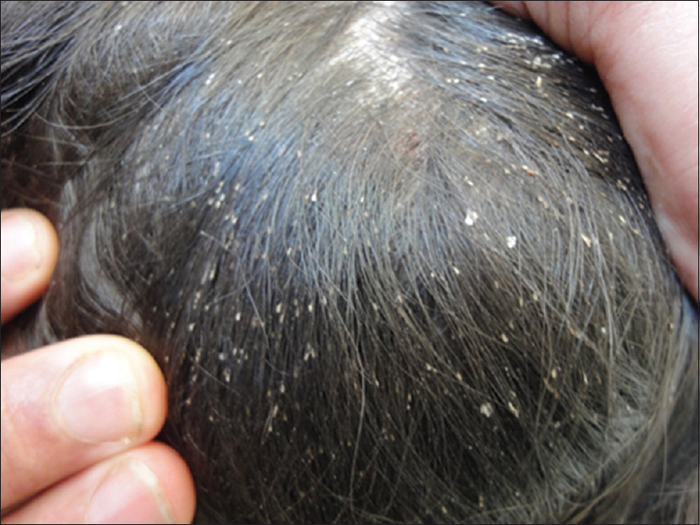
- Seborrheic Dermatitis
- Cause: Not entirely understood, but it’s associated with an overgrowth of yeast on the skin, Malassezia, and an inflammatory response.
- Symptoms: Scaly, greasy patches on the scalp, often accompanied by redness and dandruff.
- Treatment: Dandruff shampoos containing zinc pyrithione, selenium sulfide, or ketoconazole can help. In more severe cases, a doctor might prescribe topical corticosteroids or antifungal creams.
- Pediculosis Capitis (Head Lice)
- Cause: Infestation by the louse Pediculus humanus capitis.
- Symptoms: Intense itching of the scalp, visible nits (lice eggs) on hair shafts, and sometimes live lice visible on the scalp.
- Treatment: Over-the-counter or prescription lice treatments, along with meticulous combing of wet hair to remove nits.
- Piedra (Trichomycosis Nodularis)
- Cause: A fungal infection that leads to the development of hard nodules on hair shafts. It can be white (caused by Trichosporon spp.) or black (caused by Piedraia hortae).
- Symptoms: Hard nodules on the hair shaft that may weaken the hair and cause it to break.
- Treatment: Antifungal shampoos, creams, or oral medications. Affected hair may need to be cut or shaved.
Prevention of Hair Infections
- Maintain Good Hygiene: Regular washing of the hair and scalp can help prevent infections.
- Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Don’t share combs, hats, or pillows with others to prevent the spread of infections like lice or fungal spores.
- Manage Scalp Moisture: Keep your scalp dry after washing your hair, as excessive moisture can promote fungal growth.
- Use Protective Gear: In communal showers or swimming pools, wear shower caps or swim caps to reduce the risk of catching fungal infections.
When to See a Doctor
Consult a healthcare provider if:
- You experience persistent symptoms that don’t improve with over-the-counter treatments.
- The infection leads to severe pain, hair loss, or spreading sores.
- You suspect you have tinea capitis or severe folliculitis, as these conditions require prescription medication.
Proper diagnosis and treatment are crucial for effectively managing hair and scalp infections, preventing further complications, and maintaining healthy hair and scalp.



